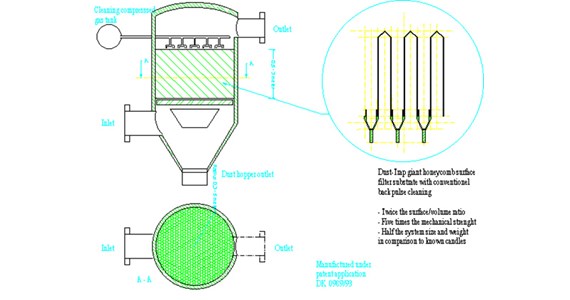
DustTrap R&D project
In modern PFCB (Pressurized Fluid Combustion Bed) plants, it is believed that the overall thermal efficiency can be increased by an extremely important few percent, for a typical set-up with a gas-turbine/generator mounted directly to the combustor outlet.
This has, until now, been very difficult as the gas, containing large amounts of solids, will erode or wear out the gas-turbine parts in an extremely short period of time. The gas in the combustor is preferably 850°C hot, controlled at 25 Bar pressure. Locating a highly efficient filter system in this environment has, until now, caused large problems. PFCB test plants rarely exceed a total power output of more than 5 MW, yet power generation is preferable with plants delivering a total power output in the range 50-100 MW.
The present invention relates to a barrier filter device, system design and the manufacturing method, for filtering solid particles from a fluid or gas containing the particles. Particulate collection on barrier filter devices occurs initially by interception and impaction of the particles as the fluid are pumped through the porous filter wall.
Partners were:
- Stobbe Tech A/S, Denmark
- Henrik Vittrup Pedersen from FLS Miljø A/S, Denmark
- DTU, Danish Technical University (Jakob W. Hoej, Lars Tinggaard Johannessen, Torsten Bove)
Title: “Development project for ceramic hot gas filters”
Funded with 1 mio € budget by Danish Department of Industry, EFP91-93
Project period: 1991 to 1994